Women and Culture
This is a website created to raise awareness and inform the public about harmful traditions and cultural norms that affect most women throughout their lives.
What is Female Genital Mutilation?
According to the World Health Organisation, female genital mutilation is the procedure where parts of the external genitalia or the whole external genitalia are removed.
Why is this done?
This procedure has no health benefits whatsoever and is a non-medical procedure that is illegal in 59 countries.
However, it is done for social and religious beliefs which are usually performed against the patient's will.
Where is it done ?
Female genital mutilation is majorly done in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia; even in countries that have legislation or laws against it. According to UNICEF, at least 200 million women in 31 different countries have undergone the procedure. The top 3 countries where women from the ages of 15-49 have undergone female genital mutilation are Burkina Faso, Djibouti, and Egypt.
What are the health risks ?
Chronic genital infections, chronic reproductive tract infections, and urinary tract infections could occur because of female genital mutilation as reported by the WHO. Urinary tract infections could lead to renal failure and later death. FGM is also associated with birth complications like postpartum hemorrhage, difficult labour, obstetric tears, and extended maternal hospital stay. It can also cause perinatal risks like prematurity and low birth weight.
What are honor killings ?
Honor killing is a crime committed that is usually done by male kin to the female kin when they are accused or suspected in engaging in behavior that could taint the family's status because it is not accepted by the surrounding community.
Why are honor killings committed ?
This crime is just another way of oppressing women and limiting their freedom. This is done by enforcing the belief that women are objects that belong to the family (especially the male kin) and not human beings entitled to equal rights to those of men
Where is it done ?
Although this crime has been suspected to be one of the crimes usually unreported or even sometimes ignored by law enforcement, it has been a pattern that it happens usually in the Middle East or South Asia mainly in India and Pakistan.
Statistics on domestic violence 2019-2020
According to UN Women, reports of domestic violence during the pandemic, especially in countries like Singapore, Cyprus, and Australia, have heightened.
However, even before the virus had spread 243 million women aged 15-49 across the world have reported sexual or physical violence by their partner.
What Is Abuse?
Abuse is the improper use of power or the act of causing harm to another. It comes in many forms such as physical, sexual, verbal. 'Abuse' became a word we hear on a daily basis and deeply common all around the world, which is catastrophic because it’s straight-up deadly aggression.
Why Is Abuse Done?
Why abuse is done is a question that is not supposed to have an answer because then we’d be giving excuses to the abusers that would make them feel okay about their crimes but thinking with perspective there are multiple reasons:
being used to having whatever they want whenever and howeversexual oppressionmaking their way through what they want by violenceindividuals being control freaks and society allowing them tobeing abused themselves beforelack of boundaries and empathy
Where Is It Done?
This is when you know it’s bad. It is done all over the world. It’s not about race, religion, or sexuality. It’s because we have a, frankly, sickening mentality thinking it's normal. South Africa is said to have the highest number of domestic violence. Countries with the highest number of abuse reports are South Africa, Botswana Lesotho, Eswatini, Bermuda, Sweden, Suriname, and Costa Rica.
All About Child Marriage
Growing up in a small town or countryside, women are expected to face early marriage. It has also been discovered that women who live in the slums experience the same issue. Usually they are uneducated. On the other hand, it is very rare to those who had accomplished their school education to experience this malpractice.
What is the prevalence of underage marriage?
Every year, 12 million females, below the age of 18, are married against their will. Studies approved that in developing countries, one in every three girls are married around the age of 18, while 12% get married before reaching 15 years old.
In which countries is underage marriage prevalent?
Niger is the most prevalent country suffering child marriage, while Bangladesh has the highest rate of girls’ marriage under 15. South Asia is home to of overall child brides worldwide; whereas, India accounts for 1/3 of the global total child marriage. Egypt is ranked 13 among countries suffering child brides. 17% Egyptian girls are married before their 18th birthday, while 2% are married before 15.
What are the causes and consequences of underage marriage?
Underage and constrained marriage often happens as a result of destitution, gender disparity, traditions and frailty. It surely contributes to getting pregnant even though they aren’t ready. As a result, there are a lot of severe side effects that may occur. Not all of them but at least several ones are most likely to happen. Such as: maternal mortality, infant mortality, premature childbirth, complications during delivery, low birthweight, HIV/AIDS and abuse along with violence.
Whether being forced or not, marriage at early age does not only affect females’ bodies, but also causes depression or financial problems. Within such created families, simply these girls have zero experience as well as not enough life skills.
Ending child marriage should aid breaking poverty cycle by allowing young females to fully share in society. Empowered and educated females definitely care for their children to raise healthier families. When girls live as girls, everybody wins.

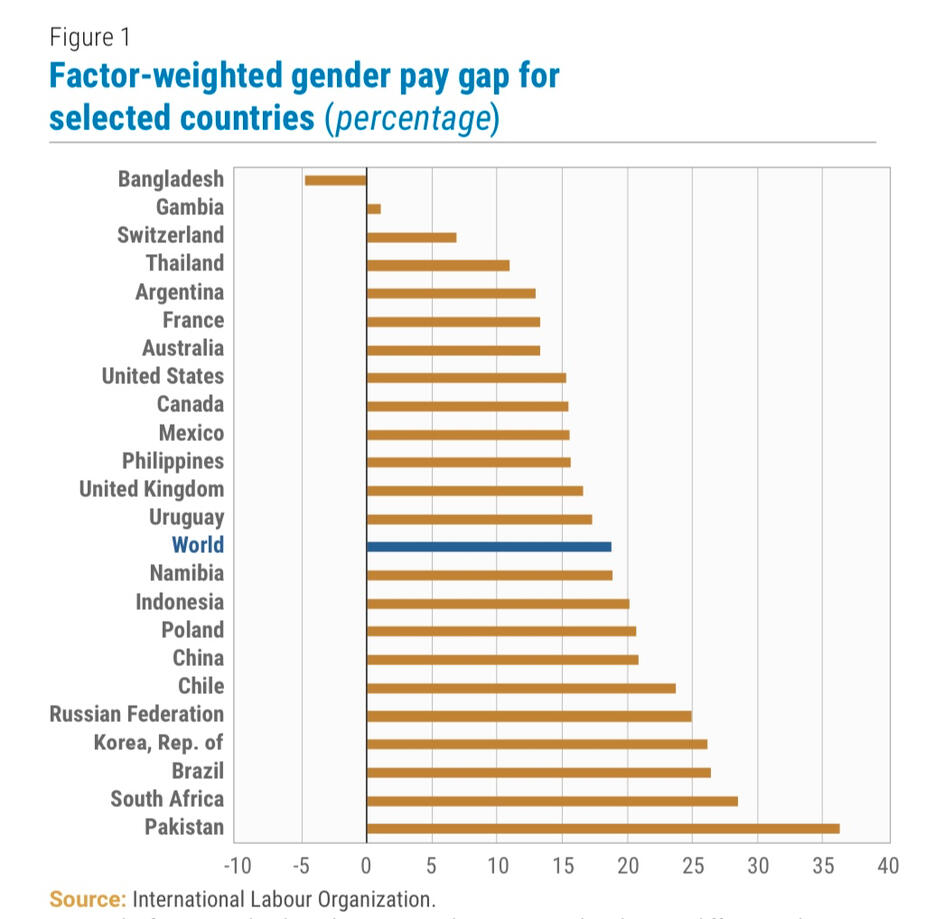
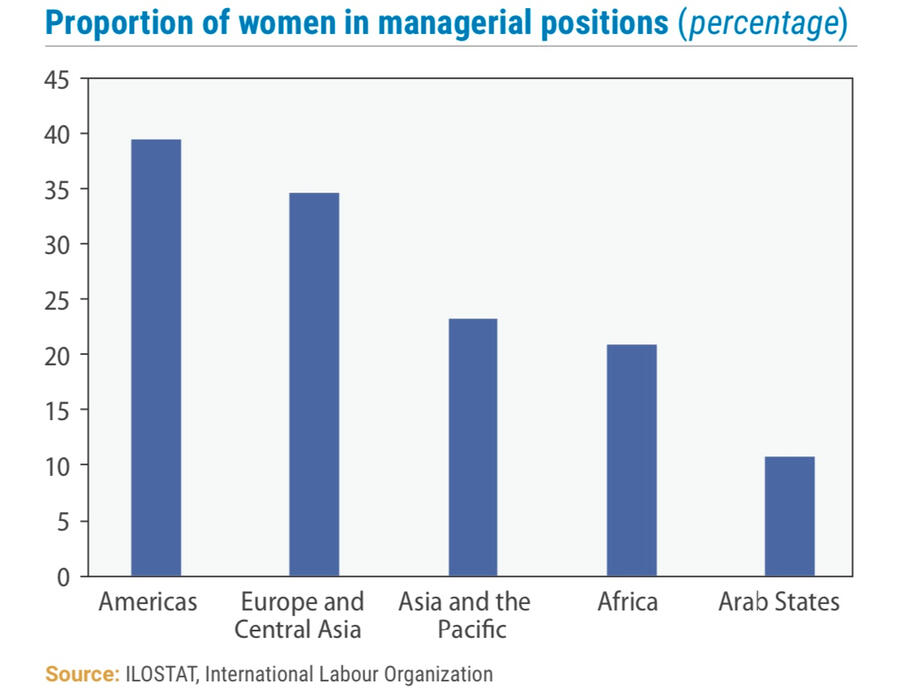
The Wage Gap and Why Women Have Less Job Opportunities
Specifically in developing countries, where there are more women in poverty, chances of women having same job opportunities as a man are slim. This is because of many factors which include but are not limited to: the disapproval of family members, illiteracy, and the stigma around women in the workplace; employees believe that women don't make sound decisions (lack leadership skills), aren't as professional and can't work efficiently while raising their kids.
In some cultures, women don't have a say on when they are married and so are forced to drop out of school at a young age. Globally, young women have the highest rate of unemployment. The ILO estimates the rate of young women participating in the labor force is only 37.1%.
Why is Women's Unemployment a Problem ?
unemployment due to lack of education or discrimination in employment stops women from having financial freedom as they now have to depend on someone else to meet their basic needs. This isn't only a problem for women as women make up 50% of the population yet some still can not contribute to national development.
Literacy Amongst The Youth
According to UNICEF, in two-thirds of countries literacy rates are almost equal for men and women. However, in developing countries- especially west and central Africa in addition to South Asia- illiterate women far outnumber men, with Sub Saharan Africa having the lowest adult female literacy rate at 57%.
How Does Culture Play A Part In This?
In societies where the female literacy rate is much lower than the male literacy rate, it is usually thought that teaching a son is a better investment than teaching a daughter because the socially accepted role for a woman is limited to raising a family and that education isn't a priority as they can get married early on.
Toxic masculinity plays a huge part in the setback of women's education, as family honor is a huge issue. The man is seen as the provider so why should a woman get an education and work? This discrimination usually begins in childhood when the son gets more attention and free time, but the daughter is forced into helping with house chores.
Why is Illiteracy a Problem ?
Illiteracy creates many problems especially for poorer women or women who live in rural areas. Their lack of education doesn't only limit their job offerings but it also stops them from contributing to educating their children as well as lowers their ability in making decisions and sometimes is a reason for women's lack of knowledge around their own health.
The struggles women face in their lifetime are endless from topics that are considered minuscule to huge topics that could be a life or death situation. Some of you might ask, how can we help? Listen. Listen to women's struggles, believe their experiences, and don't try to demean their worth. Not just because you have a sister or a mother but also because we are humans within your community who deserve just as many rights and just as much respect regardless of what demeaning traditions have brainwashed our cultures. Finally, try to donate to as many causes that you believe in as you can, even if its a small amount, and sign petitions as those small actions can change someone's life for the better.
Hotlines
Armenia
National Hotline on Domestic Violence : +374 105 428 280800 80 850
Australia
The National Sexual Assault, Family & Domestic Violence Counselling Line: 1800 737 732
Belgium
Hotline for all violence: 1712 (Flemish)
Brazil
Women’s Violence Hotline Nationwide: 1-8-0
Egypt
The female mutilation hotline: 1600 or 16021
The national council for women's complaint hotline: 01205575331- 01121997477- 01007525600
Legal services in Cairo
El Nadeem Center For Victims of Violence and Torture: [email protected], Hotline: 0100 66 624 04/ 010066 648 94
Legal services in Alexandria
Women and Development Association: (+20-3) 554 9652/ 018 301 333 26
France
Violences Femmes Info : 3919
India
Women's Helpline: 1091
Women's helpline for domestic abuse: 181
Shakti Shalini: 10920
Sakshi Violence Intervention Center: (0124) 2562336/ 5018873
Saheli: A Women's Organization:(011) 24616485
Kuwait
So far there is no domestic violence prevention law in Kuwait, and therefore no hotline.
However there are multiple volunteer organizations for women in Kuwait :
Eithar : http://eithar-kuwait.org/en/
Malaysian women’s help for domestic violence
WAO Hotline: +603 7956 3488
SMS/WhatsApp TINA: +6018 988 8058
Saudi Arabia
Abuse Hotline : 1919
Spain
Helpline for Information and Legal Advice on Gender Violence: 016
Sweden
Terrafem --->020 52 1010
Kvinnofridslinjen ----> 020 50 50 50
United Kingdom
24-hour National Domestic Abuse Helpline
0808 2000 247
USA
National Sexual Assault Hotline
1-800-656-HOPE (4673)
Sources We Used
Abolish Article 153. 2015. About | Abolish Article 153. [online] Available Here
Alami, M., 2020. Recent Killing In Lebanon Sheds Light On Honor Killings In The Country. [online] Al Arabiya English. Available Here
Brides, G., n.d. Child Marriage Around The World - Girls Not Brides. [online] Girls Not Brides. Available Here
Broster, A., 2020. Millions Of Women & Girls At Risk Of FGM In 2020, Says UNFPA. [online] Forbes. Available Here
Chandrasekhar, S., 2020. Factors affecting age at marriage and age at first birth in India. [Online] Ideas.repec.org. Available Here
GAC. 2020. Child, Early And Forced Marriage. [Online] Available Here
Global Gender Gap Report 2020. 2019. Box 1: Progress Towards Gender Equality In Wages, Where Do We Stand?. [online] Available Here
Helpline, A., n.d. Woman Abuse - Assaulted Women's Helpline. [online] Available Here
Her, P., 2020. Honor Killings Around The World. [online] ArcGIS StoryMaps. Available Here
Ilo.org. 2017. The Gender Gap In Employment: What's Holding Women Back?. [online] Available Here
Kidshealth.org. 2020. Abuse (For Teens) - Nemours Kidshealth. [online] Available Here
Mlabo- Ngcuka, P., 2020. Violence Against Women And Girls: The Shadow Pandemic. [online] UN Women. Available Here
N. Singh, R., 2016. Honor Killing | Sociology. [online] Encyclopedia Britannica. Available Here
Rainn.org. 2020. Sexual Harassment | RAINN. [online] Available Here
Right to Education Initiative. 2018. Women And Girls. [online] Available Here
Scotland, P., 2020. Harmful Traditional Practices. [online] Healthscotland.scot. Available Here
Selby, D., 2019. How Women Are Shut Out Of The Global Workforce. [online] Global Citizen. Available Here
Sos, D., El-Gaafary, M., Wahdan, M., Wassif, G., Hakim, S., Hussein, W., Hassan, A., El-Awady, M., Rady, M. and A, W., 2020. Child marriage: a major risky behavior in developing Egyptian governorates. Al-Azhar Medical Journal, 49(1), pp.305-318. Available Here
The Hotline. 2020. Domestic Violence Statistics - The Hotline. [online] Available Here
UN Women. n.d. Facts And Figures: Ending Violence Against Women. [online] Available Here
UNFPA, 2020. Female Genital Mutilation (FGM) Frequently Asked Questions. [online] UNFPA.org. Available Here
UNFPA Egypt. n.d. Female Genital Mutilation. [online] Available Here
UNICEF DATA. 2020. Female Genital Mutilation (FGM) - UNICEF DATA. [online] Available Here
Unicef.org. 2020. Ending child marriage progress and prospects. [Online] Available Here
Usaid.gov. 2020. Gender Equality And Women's Empowerment | Egypt | U.S. Agency For International Development. [online] Available Here
Women’s Aid. n.d. What Is Domestic Abuse?. [online] Available Here
World Health Organization, London School of Hygeine and Tropical Medicine, South African Medical Research Council. n.d. Global and Regional Estinates of Violence Against Women [online] Available Here
World Health Organization. n.d. Female Genital Mutilation (FGM). [online] Available Here
Worldpopulationreview.com. 2020. Rape Statistics By Country 2020. [online] Available Here
Yaya, S., Odusina, E. and Bishwajit, G., 2019. Prevalence of child marriage and its impact on fertility outcomes in 34 sub-saharan African countries. BMC International Health and Human Rights, 19(1). Available Here
First item
Second item
Third item